Are you looking for comprehensive guide to managing risks in your organization? Look no further than the NIST Risk Management Framework!
The framework provides structured approach to identifying, assessing & responding to potential risks. In this blog post, we’ll take deep dive into the components of the NIST Risk Management Framework & how it can help improve your organization’s resilience. So buckle up & get ready to become risk management expert!
What is the NIST Risk Management Framework?
The NIST Risk Management Framework (RMF) is structured approach to managing risks in an organization. It was developed by the National Institute of Standards & Technology (NIST) as set of guidelines for federal agencies, but it can be applied to any organization looking to manage its risks.
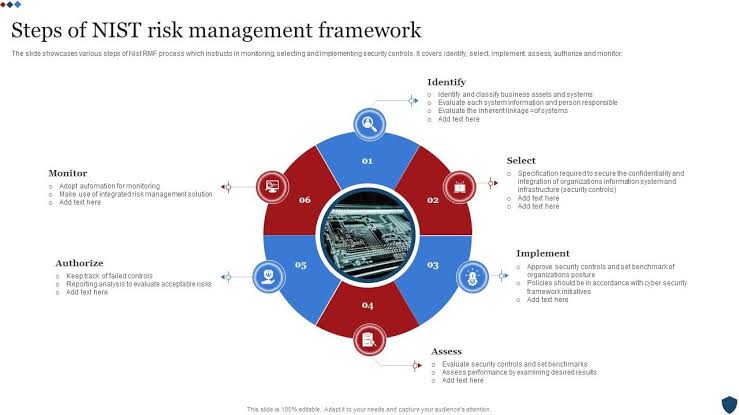
The framework consists of six steps: categorize, select, implement, assess, authorize & monitor. These steps provide methodical way to identify potential risks within an organization’s systems & processes. By following this process, organizations are better equipped to make informed decisions about how best to mitigate these risks.
One key benefit of the NIST RMF is that it provides common language for discussing risk management across different departments within an organization. This helps ensure that everyone is on the same page when it comes to identifying & mitigating potential threats.
Another important aspect of the NIST RMF is that it emphasizes continuous monitoring & improvement. Risks are constantly evolving, so organizations need to be proactive in their risk management efforts in order to stay ahead of potential threats.
The NIST Risk Management Framework provides organizations with comprehensive approach to managing their risks. By following this framework, organizations can reduce their exposure to potential threats while also improving their overall resilience.
The Components of the NIST Risk Management Framework
The NIST Risk Management Framework is made up of five main components that work together to help organizations manage & reduce their risk exposure.
The first component is the “Categorization” stage, where an organization identifies & defines its information systems based on their criticality levels. This helps them determine which systems require more attention in terms of security.
Next comes the “Selection” stage, where an organization selects the appropriate security controls for each system based on their categorization. These controls can include physical & technical measures such as firewalls, encryption protocols, or access control policies.
Once selected, these controls are implemented during the “Implementation” stage. This involves putting in place all necessary equipment & processes required to enforce these security controls effectively.
The next phase is “Assessment,” which involves testing whether installed security measures are functioning correctly & assessing any potential weaknesses or vulnerabilities that need further addressing.
Finally comes the ongoing monitoring phase known as “Authorization.” During this process, organizations continuously monitor their systems’ performance & overall risk posture by conducting audits periodically while assessing new risks continually.
Every one of these five components plays crucial role in establishing robust Risk Management Framework within an organization’s cybersecurity strategy to keep it safeguarded from cyber threats constantly emerging daily.
The National Strategy for Homeland Security | Chapter 4: Resilience & Risk Management
The National Strategy for Homeland Security’s fourth chapter focuses on resilience & risk management. It highlights the importance of understanding, assessing & managing risks that could potentially harm critical infrastructure or cause significant disruptions to government operations.
One key point in this chapter is the emphasis on integrating risk management into all aspects of an organization’s decision-making process. By doing so, organizations can better identify potential threats & vulnerabilities while also creating culture of preparedness.
Another important concept outlined in this chapter is the need for contingency planning. This involves developing strategies to respond effectively & efficiently to incidents when they occur.
Furthermore, post-incident review & lessons learned are integral components of effective risk management. Organizations must analyze their response efforts following an incident to identify areas where improvements can be made.
Chapter 4 provides valuable insights into how organizations can strengthen their resilience through comprehensive risk management practices.
Risk Identification & Assessment
Risk identification & assessment is crucial element of the NIST Risk Management Framework. The purpose of this phase is to identify potential risks that could impact an organization’s operations, assets, or overall mission.
The first step in risk identification is to define the scope of the analysis. This involves identifying all relevant systems, applications, data repositories & physical assets that will be included in the analysis.
Once the scope has been defined, it’s time to start identifying potential risks. These can come from variety of sources including internal vulnerabilities such as outdated software or inadequate access controls; external threats such as cyber attacks or natural disasters; & operational risks like human error or supply chain disruptions.
After identifying potential risks, they must be assessed based on their likelihood & potential impact. This helps organizations prioritize which risks need to be addressed first.
Organizations must determine whether they are willing to accept any residual risk after implementing mitigation measures. If not, additional controls may need to be implemented until an acceptable level of risk has been achieved.
Risk identification & assessment is critical component of effective cybersecurity management that enables organizations to proactively address vulnerabilities before they become major issues.
Hazard Identification & Risk Analysis
In the NIST Risk Management Framework, hazard identification & risk analysis are critical components in identifying potential threats & vulnerabilities that could impact an organization’s operations. This process involves assessing the likelihood of threat occurring, as well as its potential impact on the system or information being protected.
To identify hazards & assess risks, organizations must first understand their assets, including hardware, software, data, facilities, personnel & other resources. By understanding what is at stake & where vulnerabilities may exist within these assets can allow for better decision making when it comes to prioritizing security measures.
Once hazards have been identified, organizations must analyze the risks associated with each one by evaluating potential consequences such as financial loss or damage to reputation. This helps prioritize mitigation efforts based on the level of risk posed by each hazard.
Effective hazard identification & risk analysis allows organizations to proactively manage threats before they occur rather than reacting after an incident has already taken place.
Response Planning
Response planning is critical component of the NIST Risk Management Framework. This stage involves developing strategies & procedures to respond effectively to identified risks & hazards. The goal of response planning is to minimize the impact of an incident by quickly & efficiently addressing the situation.
During this phase, organizations must consider various factors that could influence their response efforts, such as resource availability, communication channels, regulatory requirements & stakeholder expectations.
It’s important to note that response planning isn’t just about reacting to an incident – it also involves proactive measures such as preventative controls & ongoing monitoring. By having well-defined response plans in place, organizations can reduce the likelihood of incidents occurring in the first place or mitigate their impact if they do occur.
Effective response planning requires collaboration between stakeholders across different departments or functions within an organization. It should be continuous process that evolves over time as new threats emerge & existing ones are addressed.
Contingency Planning
Contingency planning is critical component of any risk management framework. This process involves identifying potential emergencies or disasters that could impact an organization’s operations & developing plans to address them. The goal of contingency planning is to minimize the impact of unexpected events & ensure that an organization can continue its essential functions as smoothly as possible.
In order to develop effective contingency plans, organizations must first identify potential risks & vulnerabilities. These may include natural disasters such as hurricanes or earthquakes, cyber attacks, power outages, or supply chain disruptions. Once these risks have been identified, organizations can begin to develop specific strategies for responding to each scenario.
Contingency plans should outline clear procedures for responding to emergencies, including communication protocols & evacuation procedures if necessary. Organizations should also establish backup systems in case primary infrastructure fails during crisis.
It’s important for organizations to regularly review & update their contingency plans based on changes in their operations & the evolving threat landscape. By doing so, they can help ensure that they are prepared for whatever challenges come their way.
Post-Incident Review & Lessons Learned
Post-Incident Review & Lessons Learned is the final component of the NIST Risk Management Framework that assesses organizational response, identifies areas for improvement & helps prevent similar incidents in the future. The review process involves evaluating all aspects of an incident, from its cause to its resolution, to determine what went wrong & what could have been done differently.
The goal of post-incident review is not to assign blame but rather to identify opportunities for improvement. By analyzing how risk event unfolded & identifying gaps in planning or execution, organizations can refine their risk management strategies & better prepare for future contingencies.
A comprehensive post-incident review should address questions such as: What were the root causes of the incident? Were there any warning signs that could have been detected earlier? Did existing policies or procedures fail during the response effort? What worked well during the response effort?
Once these questions are answered, lessons learned should be identified & documented so that they can inform future risk management activities. These lessons may include recommendations related to training programs, internal communication protocols or updates to policies & procedures.
Conducting effective post-incident reviews is critical for building resilient organization capable of quickly responding to emerging risks while minimizing harm.
Conclusion
In today’s fast-paced & ever-changing technological landscape, risk management is more important than ever before. It is essential to ensure that organizations remain secure, resilient & ready to face any challenge that comes their way.
The NIST Risk Management Framework provides comprehensive approach to identifying, assessing, responding to & recovering from potential risks. The framework helps organizations understand the risks they face & develop proactive measures to manage them.
By implementing the components of the NIST Risk Management Framework in their operations, organizations can effectively identify threats & vulnerabilities while developing strategies for mitigation. They can also proactively plan responses should an incident occur.
Ultimately, with robust risk management strategy in place utilizing the NIST Risk Management Framework guidelines as foundation – businesses can achieve resilience even amidst unprecedented challenges In this sense future-proofing themselves against unforeseen events down the road.
So if you haven’t already done so – it may be time to integrate these principles into your organization’s security policies & procedures so you too can stay ahead of emerging threats thus taking steps toward securing organizational safety at all levels!
Nice
Omg